13.2.3. Evidence for the existence of nuclear energy level
>> 1. The Gamma ray spectra change
2. The change in Kinetic Energy of the Alpha Particles
13.2.4. Describe Beta Decay including the existence of the neutrino
>> Beta Decay is the loss of fast moving electron. The experiment that showed a continuous spectrum of energy for Beta Decay appeared to contradict the principle of conservation of energy. it had been found to be continuous because of a continuous spectrum of energy, the disappearance of the kinetic energy and momentum. This is due to neutrino which is too small too measure.
Monday, 31 January 2011
Sunday, 30 January 2011
Nuclear Physics 13.2.1 and 13.2.2
13.2.1 Explain how the radii of nuclei may be estimated from charged particle scattering experiment
>> In the charged particle scattering experiment, the particle that is repelled back from the gold nucleus will have to be at rest before it changes direction. Rutherford proposes that he could use this fact (energy conservation in this situation) to estimate the size of the nucleus. This is because when the particle is at rest, its KE will be balanced by the electric potential energy due to the repulsive electrostatic force.


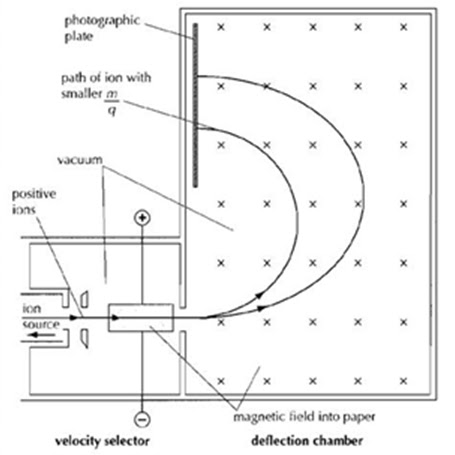
13.2.2. Describe how the masses of nuclei may be determined using a Bainbridge mass spectrometer.
>> The principle of Bainbridge mass spectrometer is to use the magnetic field to deflect moving ions of a substance. If a moving ion enters a constant magnetic field, B, it will follow a circular path. Because the radius of the circular path depends on the mass of the ion, a larger mass ion will travel in a larger circular path. Thus the principle can be used to determine the masses of nuclei:

>> In the charged particle scattering experiment, the particle that is repelled back from the gold nucleus will have to be at rest before it changes direction. Rutherford proposes that he could use this fact (energy conservation in this situation) to estimate the size of the nucleus. This is because when the particle is at rest, its KE will be balanced by the electric potential energy due to the repulsive electrostatic force.


13.2.2. Describe how the masses of nuclei may be determined using a Bainbridge mass spectrometer.
>> The principle of Bainbridge mass spectrometer is to use the magnetic field to deflect moving ions of a substance. If a moving ion enters a constant magnetic field, B, it will follow a circular path. Because the radius of the circular path depends on the mass of the ion, a larger mass ion will travel in a larger circular path. Thus the principle can be used to determine the masses of nuclei:


Monday, 24 January 2011
Sunday, 23 January 2011
Sunday, 16 January 2011
12.3 Transmission of electrical power
12.3.1 Outline the reasons for power losses in transmission lines and real transformers.
- Power losses in transmission lines and real transformers occur because energy is dissipated when they warm up, since they have a resistance. Having a thick wire can decrease the resistance occurred.
- Flux losses are caused by magnetic leakage. a transformer is only 100% efficient if all of the magnetic flux that is produced by the primary links with the secondary
- Flux losses are caused by magnetic leakage. a transformer is only 100% efficient if all of the magnetic flux that is produced by the primary links with the secondary
12.3.2 Explain the use of high-voltage step-up and step-down transformers in the transmission of electrical power.
According to the formula P=I^2R, the power lost in wires is dependent on the current. Step-up transformers can therefore be used to lower the current without having to loose any power as well as minimizing dissipation. The high voltage created however is too dangerous to be use at home thus, the voltage is at the end stepped down so that it can be use safely by consumers.
12.3.4 Suggest how extra-low-frequency electromagnetic fields, such as those created by electrical appliances and power lines, induce currents within a human body.
Photons sent out from electromagnetic fields are too low to ionize anything. However it can still induce currents in the human body.
12.3.5 Discuss some of the possible risks involved in living and working near high-voltage power line
- statistical evidence revealed that there are higher risks of getting leukemia or cancer when living near power lines.
- changing extra-low-frequency electromagnetic fields are theoretically able to induce currents within any conductor, including human bodies nearby
- current experimental evidence suggests that low-frequency fields do not preferentially harm genetic material
- risks are likely to be dependent on current, A.C frequency and length of exposure
Monday, 10 January 2011
Alternating Current
12.2.3 Describe the effect on the induced emf of changing the generator frequency.
12.2.4 Discuss what is meant by the root mean squared (rms) value of an alternating current or voltage
The rms is the square root of the mean of the square. The rms value of an alternating current (or voltage) is the value of the direct current (or voltage) that dissipates power in a resistor at the same rate.
12.2.5 State the relation between peak and rms values for sinusoidal currents and voltages.

12.2.4 Discuss what is meant by the root mean squared (rms) value of an alternating current or voltage
The rms is the square root of the mean of the square. The rms value of an alternating current (or voltage) is the value of the direct current (or voltage) that dissipates power in a resistor at the same rate.
12.2.5 State the relation between peak and rms values for sinusoidal currents and voltages.
Sunday, 9 January 2011
Alternating current
12.2.1: Describe the emf induced in a coil rotating within a uniform magnetif field:
If the coil is rotating with a constant speed, the emf generated is sinusoidal and affected by four factors:
Many turns of coils of wire are wound around an object which then can be rotate in a magnetic field. The axle is rotated and an induced emf is formed, creating a current
If the coil is rotating with a constant speed, the emf generated is sinusoidal and affected by four factors:
- The number of turns of coil.
- The angle of flux cutting (90 degrees).
- The speed of flux cutting.
- The magnetic field strength.
Many turns of coils of wire are wound around an object which then can be rotate in a magnetic field. The axle is rotated and an induced emf is formed, creating a current
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)








